Planning for Retirement 2024: Estimating Your Social Security Benefits at Age 65
Are you ready for retirement? As you approach the age of 65, it's important to start planning and estimating your Social Security benefits. Social Security benefits can provide a significant source of income during your retirement years, but understanding how much you'll receive is crucial for your financial planning.
Today I’ll guide you through a step-by-step process of estimating your Social Security benefits at age 65. We'll break down the factors that influence your benefits, such as your earnings history, yearly income, and the age at which you decide to start claiming benefits. We'll also discuss how to access your Social Security statement and use it to get an estimate of your future benefits.
Knowing how much you can expect from Social Security can help you make informed decisions about your retirement savings and other sources of income. So, let's dive in and get a better understanding of how to estimate your Social Security benefits at age 65.
Remember, planning ahead is key to a comfortable and worry-free retirement.
What is Social Security?
Social Security is a federal government program designed to provide financial support to retired individuals, disabled workers, and the surviving dependents of deceased workers. It was established in 1935 as part of the New Deal legislation (thanks to President Franklin D. Roosevelt) to help alleviate poverty among the elderly and provide a safety net for those who are unable to work.
You probably think of Social Security as a retirement program, but there are several other reasons someone might receive benefits:
They have a qualifying disability
They are the spouse or child of someone receiving benefits
They are the divorced spouse of someone receiving or eligible to receive Social Security
They are the spouse or child of a worker who died
They are a divorced spouse of a worker who died
They are a dependent parent of a worker who died
As of June 2022, about 182 million American workers paid into Social Security and about 66 million Americans received monthly Social Security benefits.
Paying for Social Security
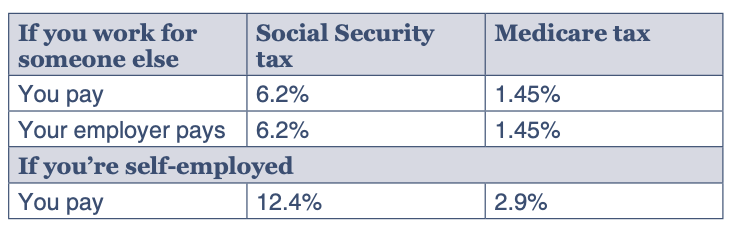
The Social Security program is funded through payroll taxes, with both employees and employers contributing a portion of their earnings.
In 2024, you only pay Social Security taxes on your first $168,600 of income. While you do not pay Social Security tax on income above that amount, you pay Medicare tax on all of your earnings.
Payroll Taxes (or FICA, the Federal Insurance Contributions Act) are deducted from each paycheck.
These contributions go into a trust fund, which is used to pay benefits to eligible individuals when they reach retirement age or experience a qualifying event.
Eligibility for Social Security benefits
To be eligible for Social Security retirement benefits, you must have earned enough credits throughout your working years. Credits are earned based on the income you earn and the amount of Social Security taxes you pay. Generally, you need a total of 40 work credits (10 years of work) to qualify for retirement benefits.
The number of credits you earn each year is based on your earnings. In 2024, you earn one credit for each $1,730 of earnings, up to a maximum of four credits per year. The exact amount needed for a credit changes each year, so it's important to stay updated on the current requirements.
How are Social Security Benefits calculated?
Your Social Security benefits are calculated based on your average indexed monthly earnings (AIME) and the primary insurance amount (PIA). The AIME is determined by taking your highest 35 years of indexed earnings and dividing it by the number of months in those years.
The PIA is the monthly benefit you would receive if you start claiming benefits at your full retirement age (FRA). The FRA is the age at which you are eligible to receive full Social Security benefits, which is currently 66 for those born between 1943 and 1954. It gradually increases to 67 for those born in 1960 or later.
To calculate your PIA, the Social Security Administration applies a formula to your AIME. The formula gives different weight to different portions of your earnings, with lower-earning years getting a higher percentage included in the calculation.
Estimating your Social Security benefits at age 65
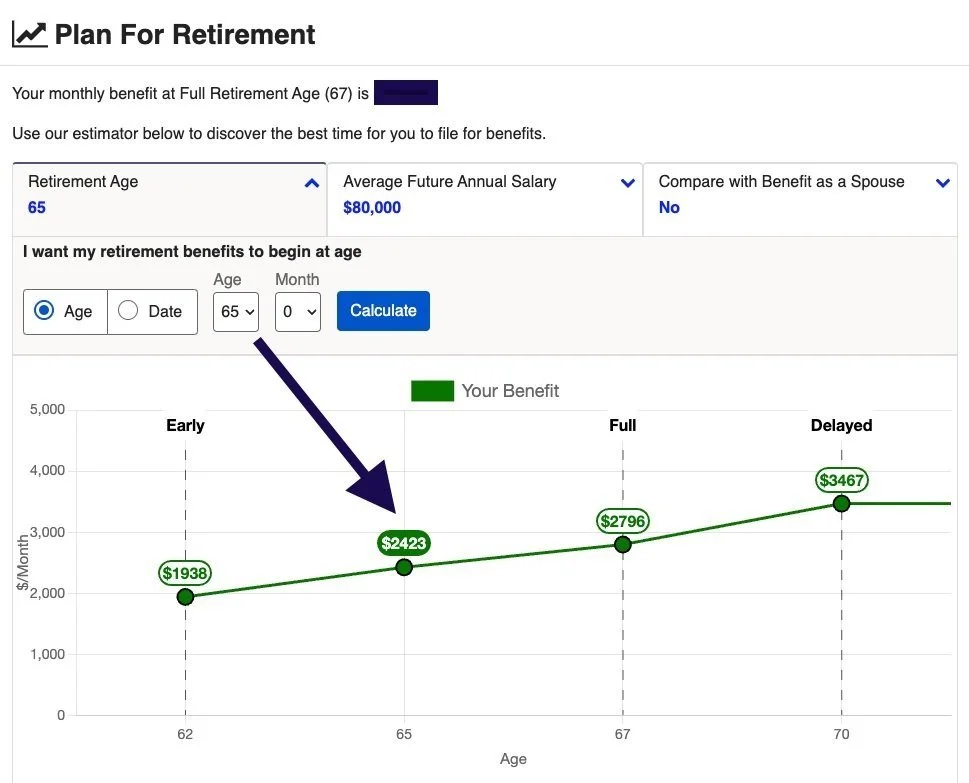
Estimating your Social Security benefits at age 65 can give you a good idea of how much income you can expect during your retirement years. The Social Security Administration provides an online tool called the Retirement Estimator, which allows you to get an estimate of your future benefits based on your earnings history.
To use the Retirement Estimator:
1. Create your my Social Security account.
2. Scroll down to the “Plan For Retirement” section (screenshot below) after you sign in. You’ll see your estimated monthly benefit automatically displayed at your full retirement age, early at age 62, and delayed at age 70.
3. Click the drop-down arrow next to “Retirement Age” and select when you want your retirement benefits to begin (by age or date). The tool will then generate an estimate of your monthly benefit amount at different claiming ages. You can even change your average future annual salary to see what impact it makes on your benefit and run estimates for a spousal benefit.
Retirement Estimator in my Social Security
It's important to note that the estimates provided by the Retirement Estimator are based on your current earnings and the assumption that you'll continue earning at the same rate until you retire. If your income is expected to change significantly in the future, the estimates may not be entirely accurate.
Factors that can affect your Social Security benefits
Several factors can affect the amount of Social Security benefits you receive. One of the most significant factors is the age at which you start claiming benefits. You can start claiming benefits as early as age 62, but your monthly benefit amount will be permanently reduced if you claim before your full retirement age.
“If you turn 62 in 2024, your benefit would be about 30% lower than it would be at your full retirement age of 67.” - Social Security Administration
On the other hand, if you delay claiming benefits beyond your full retirement age, your benefit amount will increase by 8% for each full year you delay your Social Security benefits. The increase is known as a delayed retirement credit, and it can continue to accumulate until you reach the age of 70. After that, there is no additional increase for delaying claiming benefits.
Your earnings history also plays a role in determining your Social Security benefits. The higher your earnings, the higher your benefits are likely to be. The Social Security Administration takes into account your highest 35 years of indexed earnings when calculating your benefits. If you have fewer than 35 years of earnings, the calculation will include zero for the missing years, which can lower your benefit amount.
Strategies to maximize your Social Security benefits
If you want to maximize your Social Security benefits, there are a few strategies you can consider. Here are a few tips:
Work until your full retirement age. Your Social Security benefits are based on your average earnings over the top 35 years of your working life. This means that the longer you work, the higher your average earnings will be and the higher your Social Security benefits will be.
Earn a higher income. Your Social Security benefits are also based on your average earnings. This means that the more you earn, the higher your Social Security benefits will be.
Delay claiming benefits until age 70. By doing so, you can take advantage of the delayed retirement credits and increase your monthly benefit amount.
Coordinate spousal benefits. If you are married, you may be eligible for spousal benefits. Spousal benefits are equal to 50% of your spouse's full retirement benefit.
Good to know: If you're still working and earning income while receiving Social Security benefits before your full retirement age, your benefits may be subject to the earnings test. In 2024, the earnings test reduces your benefits by $1 for every $2 you earn above $22,320 (or $1,860 per month).
Other sources of retirement income
While Social Security benefits can provide a significant portion of your retirement income, it's important to consider other sources as well. Building a diversified retirement portfolio can help ensure you have enough income to support your desired lifestyle.
Some common sources of retirement income include:
Personal savings and investments. Building a nest egg through savings and investments can provide additional income during retirement. Consider working with a financial advisor to create a retirement plan that aligns with your goals and risk tolerance.
Employer-sponsored retirement plans. If you have access to an employer-sponsored retirement plan, such as a 401(k) or a pension plan, make sure to contribute regularly. Take advantage of any employer matching contributions to maximize your savings.
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs). IRAs offer tax advantages and can be a valuable tool for retirement savings. Depending on your income level, you may be eligible for a traditional IRA or a Roth IRA. Consult with a financial advisor to determine the best option for your situation.
Part-time work. Many retirees choose to work part-time during their retirement years. Not only does it provide additional income, but it can also help you stay active and engaged. Consider exploring part-time opportunities that align with your interests and skills.
Rental income. If you own property, renting it out can be a source of passive income. Whether it's a vacation home or an investment property, rental income can supplement your retirement savings.
Importance of early retirement planning
Planning for retirement should start as early as possible. The decisions you make in your early earning years can have a significant impact on your Social Security benefits and overall retirement income.
By estimating your Social Security benefits at age 65, you can gain valuable insights into your future financial situation. This information can help you make informed decisions about saving and investing, as well as adjust your retirement planning strategies if needed.
Remember, the earlier you start saving and planning for retirement, the more time you have to build a substantial nest egg. Take advantage of the resources available to you, such as the Social Security Administration's online tools and financial advisors, to ensure you're on the right track.
Conclusion
Estimating your Social Security benefits at age 65 is an essential step in retirement planning. By understanding the factors that influence your benefits and using tools like the Retirement Estimator, you can gain valuable insight into your future income.
Remember to consider other sources of retirement income, such as personal savings, employer-sponsored retirement plans, and part-time work. Building a diversified retirement portfolio can help ensure you have enough income to support your desired lifestyle.
Start planning for retirement early and make informed decisions based on your estimated Social Security benefits. With proper planning and financial management, you can enjoy a comfortable and worry-free retirement.
To your Atomic Retirement,
Ryan Kilkenny
P.S. If you have a question or would like help with your Social Security strategy, you can schedule an appointment here.